Director of the Department
| Name |
Ayumi Okada |
| Specialist/Certified Physician |
Board Certified Pediatrician
Board certified child mental health medical specialist
Board Certified Pediatric Psychosomatic Medicine Physician
|
| Specialty |
Child Psychosomatic Medicine |
The mind and body are closely connected. Children are in the process of mental and physical development and are easily affected by psychosocial stress, resulting in the appearance of various physical symptoms. In addition, mental symptoms such as anxiety and depression, as well as behavioral problems such as truancy, may also appear due to the distress and daily life obstacles associated with physical illness. Based on “psychosomatic medicine,” our department strives to understand children comprehensively from a BioPsychoSocial perspective and to treat them in cooperation with their families, schools, and other surrounding communities.
Scope of Target Diseases
Prolonged physical symptoms
- Orthostatic Dysregulation
- Chronic headaches
- Functional gastrointestinal disorders(e.g. irritable bowel syndrome)
Physical symptoms that also require psychological support
- Eating disorders
- Chronic pain
- Chronic illnesses that affect daily life
- Childcare counseling
Mental and behavioral symptoms
- Difficulty going to preschool or school anxiety specific fears, etc.
Others
- Nocturia, Trichotillomania, nail biting, etc.
Features and Description of Medical Care
診療内容

Pediatricians and psychologists work together to provide medical care. Outpatient care is by appointment only and lasts 30-60 minutes per patient. We provide consultation for children with chronic diseases and their families, and support for those who are hospitalized for a long period of time in cooperation with other departments and divisions. Our approach is based on both mental and physical aspects. For children, we provide lifestyle guidance, relaxation, counseling, cognitive-behavioral therapy, play therapy, drawing therapy, and sandplay therapy. In addition, we also position the family as a collaborator in the treatment, and conduct family interviews and parent training in parallel. Non-verbal psychotherapy such as sandplay therapy may be effective for younger children and children who have difficulty expressing themselves verbally.
Orthostatic Dysregulation(OD)
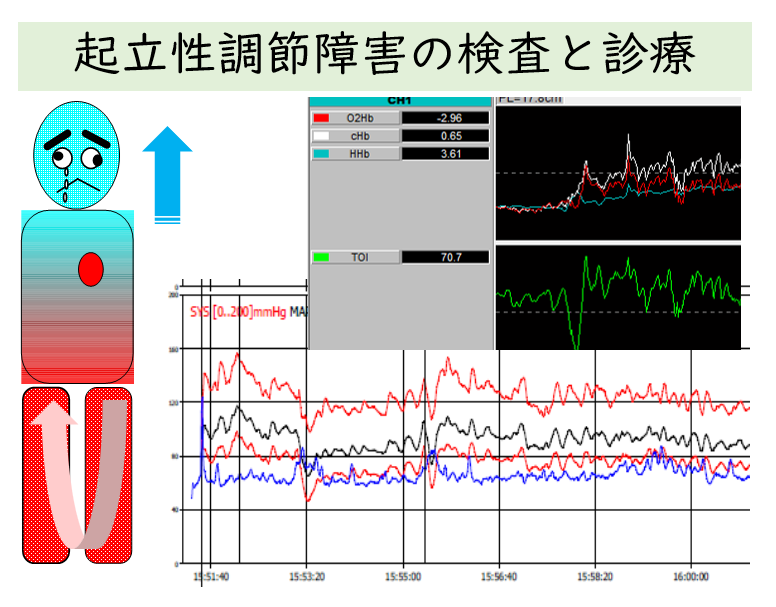
We provide lifestyle guidance, pharmacotherapy, and school collaboration for treatmet. Using Finometer MIDI and NIRS to continuously measure blood pressure and cerebral blood flow in a non-intensive, non-hematogenous manner. The painless testing method allows regular evaluation of the condition, leading to a more detailed diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Eating disorder

Family-based treatment (FBT) is effective for patients with eating disorders who are younger than 19 years old and have been diagnosed within 3 years of the onset of the disorder. FBT is based on the principles of (1) not seeking causes (agnosticism), (2) non-authoritarian attitude, (3) externalization of disease (separating the patient from the disease), (4) empowerment of the family, and (5) present-oriented and pragmatic approach.
Initial consultation is for children up to junior high school age.
About Reserch
- Okada A, Shigeyasu Y, Fujii C, et.al. Psychogenic fever and neurodevelopmental disorders among Japanese children. Biopsychosoc Med. 2024 Dec 18;18(1):23.
- Shigeyasu Y, Okada A, Fujii C, et.al.Quality of life and physical/psychosocial factors in children and adolescents with orthostatic intolerance. Biopsychosoc Med. 2023 Jun 12;17(1):23.
- Sugihara A, Okada A, Horiuchi M, et.al. Evaluating the Coping Behavior of Children with Psychosomatic Disorders under Frustrating Situations Simulated Using the Rosenzweig Picture-Frustration Study.Acta Med Okayama. 2023 Apr;77(2):185-192.
- Nagamitsu S, Kanie A, Sakashita K, et.al. Adolescent Health Promotion Interventions Using Well-Care Visits and a Smartphone Cognitive Behavioral Therapy App: Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022 May 23;10(5):e34154.
Medical Treatment Results
| Patients seen in FY2024 (actual number, not including duplicates) |
| 1.Psychosomatic disorders |
Functional somatic symptoms 44 |
orthostatic dysregulation, etc. 102 |
| Secondary disorders of chronic diseases 41 |
Perinatal and terminal stage 5 |
| 2.Mental and behavioral disorders |
Adjustment disorder, anxiety, etc. 39 |
Eating disorder, sleep disorder, etc. 56 |
| Intellectual disorder, autistic spectrum disorder 31 |
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, tic disorder 32 |
| 3.Problems arising from diverse backgrounds |
Non-attendance at school 21 |
Self-harm, problematic behavior 18 |


 We provide lifestyle guidance, pharmacotherapy, and school collaboration for treatmet. Using Finometer MIDI and NIRS to continuously measure blood pressure and cerebral blood flow in a non-intensive, non-hematogenous manner. The painless testing method allows regular evaluation of the condition, leading to a more detailed diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
We provide lifestyle guidance, pharmacotherapy, and school collaboration for treatmet. Using Finometer MIDI and NIRS to continuously measure blood pressure and cerebral blood flow in a non-intensive, non-hematogenous manner. The painless testing method allows regular evaluation of the condition, leading to a more detailed diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Family-based treatment (FBT) is effective for patients with eating disorders who are younger than 19 years old and have been diagnosed within 3 years of the onset of the disorder. FBT is based on the principles of (1) not seeking causes (agnosticism), (2) non-authoritarian attitude, (3) externalization of disease (separating the patient from the disease), (4) empowerment of the family, and (5) present-oriented and pragmatic approach.
Family-based treatment (FBT) is effective for patients with eating disorders who are younger than 19 years old and have been diagnosed within 3 years of the onset of the disorder. FBT is based on the principles of (1) not seeking causes (agnosticism), (2) non-authoritarian attitude, (3) externalization of disease (separating the patient from the disease), (4) empowerment of the family, and (5) present-oriented and pragmatic approach.